√100以上 d^2y/dx^2-y=2/1 e^x 115258-D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2
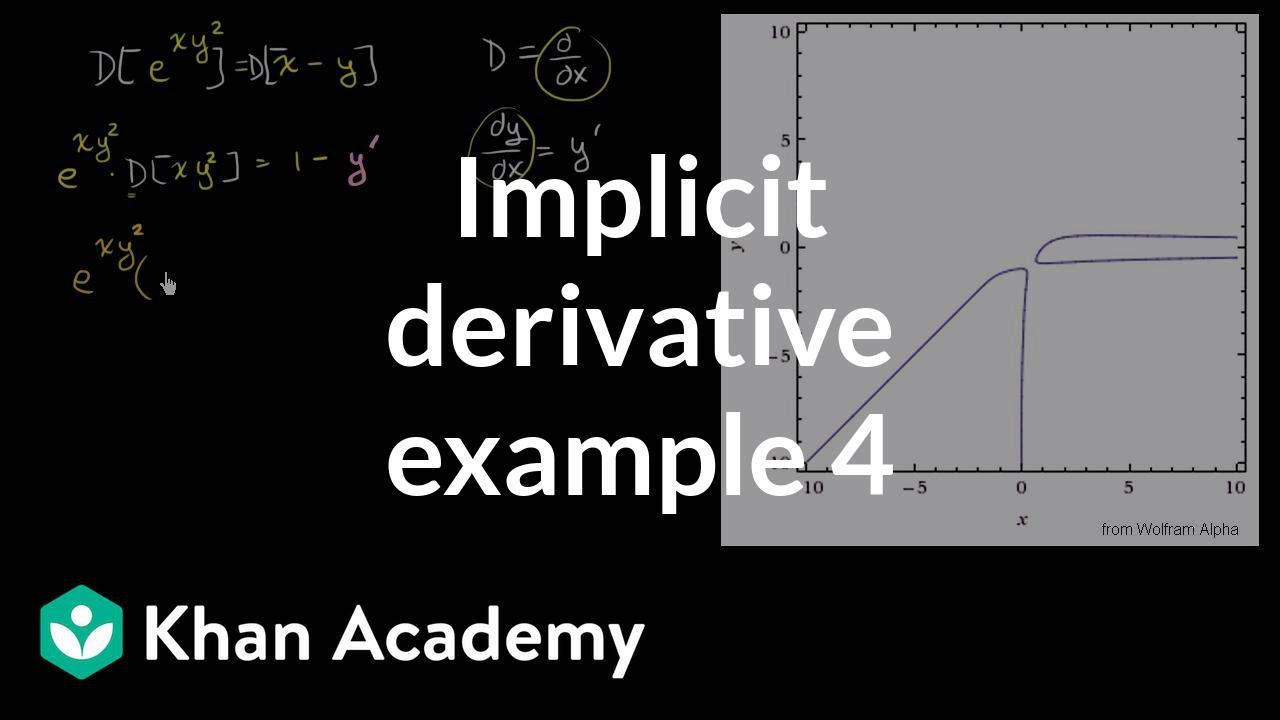
Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy
Given (D^2 D 4) y = e^2x Eq 1 To find a particular integral Let us look for it in the form of y = A e^2x Substituting in EQ 1, we get (4A 2A 4A) e^2x = e^2x OR, 10A = 1 OR, A = 1/10 Answer One particular integral of the given equation is y=e^(2x) / 10 Answer dy/dx = Stepbystep explanation e^ (xy) − y² = e^ (−4) To get dy/dx, we will differentiate with respect to x applying both chain rule and product rule Thus;
D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2
D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2-Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystepTo Find \(\rm \left(\dfrac{d^2x}{dy^2}\right) \times \left(\dfrac{d^2y}{dx^2}\right)\) y = e x Differentiating with respect to x, we get \(⇒ \rm \dfrac{dy}{dx} = e^x\) Again differentiating with respect to x, we get \(⇒ \rm \dfrac{d^2y}{dx^2} = e^x\) (1) Again, y = e x Taking log both sides, we get ⇒ log y = log e x ⇒ log y = x

If Y E Msin 1 X Prove That 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx M 2y Youtube
Question d the specific solution of the differential equation dy/dx= 2y/x^2 with condition y(−2) = e Swap the 2y and the dx integrate both sides Let C = C 1 Substitute condition y(2)=e, which means substitute x=2 and y=e Substitute C = 0 Rewrite as an exponential EdwinPlease Subscribe here, thank you!!!Ad by Project Baseline Join an athome depression study Seeking participants who are currently on medication for depression Learn More 3 Answers Best Prashant Sharma, Btech from Greater Noida Institute of Technology Answered 1
Concept Given equation is d 2 y d x 2 16 y = 0 This is a homogeneous second order differential equation, So (D 2 16)y = 0 D 2 = m 2 ⇒ m 2 16 = 0 ⇒ m = ± 4i = 0 ± 4i Solution is given as in this case roots are complex, m = α ± i β y = (C 1 cos βx C 2 sin βx) e αx0 votes 1 answer Using the method of undetermined coefficients solve d^2y/dx^2 2dy/dx 3y = x^2 cosx Anyways, in both cases, the two constants A and B must remain You cannot eliminate one at this stage of the calculus Second At the end, it is not correct to add a new constant D, because (df/dx)/f is not an integral Finally, you will obtain an expression y (x) with, into it, one parameter on the form C= (A/B), or C= (B/A), which can be
D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  | 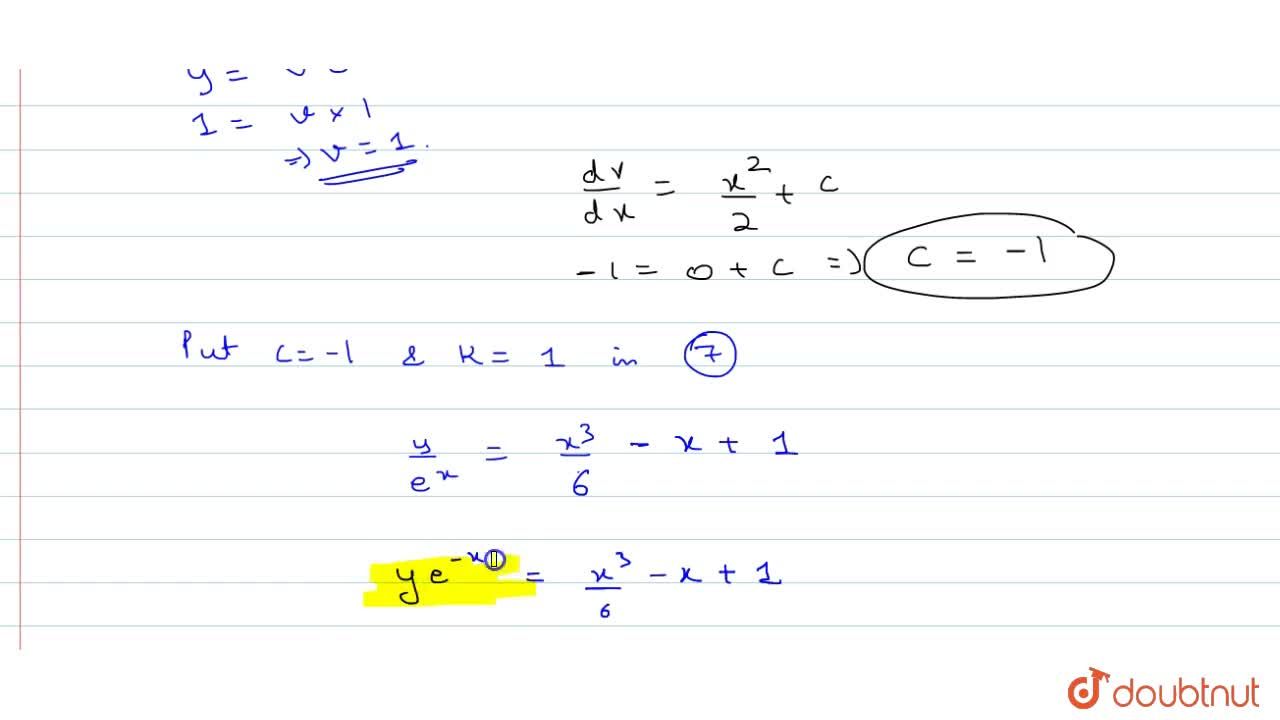 |
 | ||
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
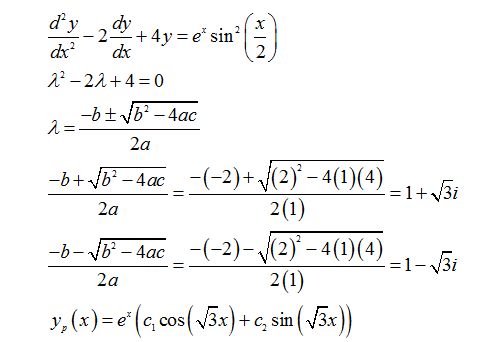 |  | |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
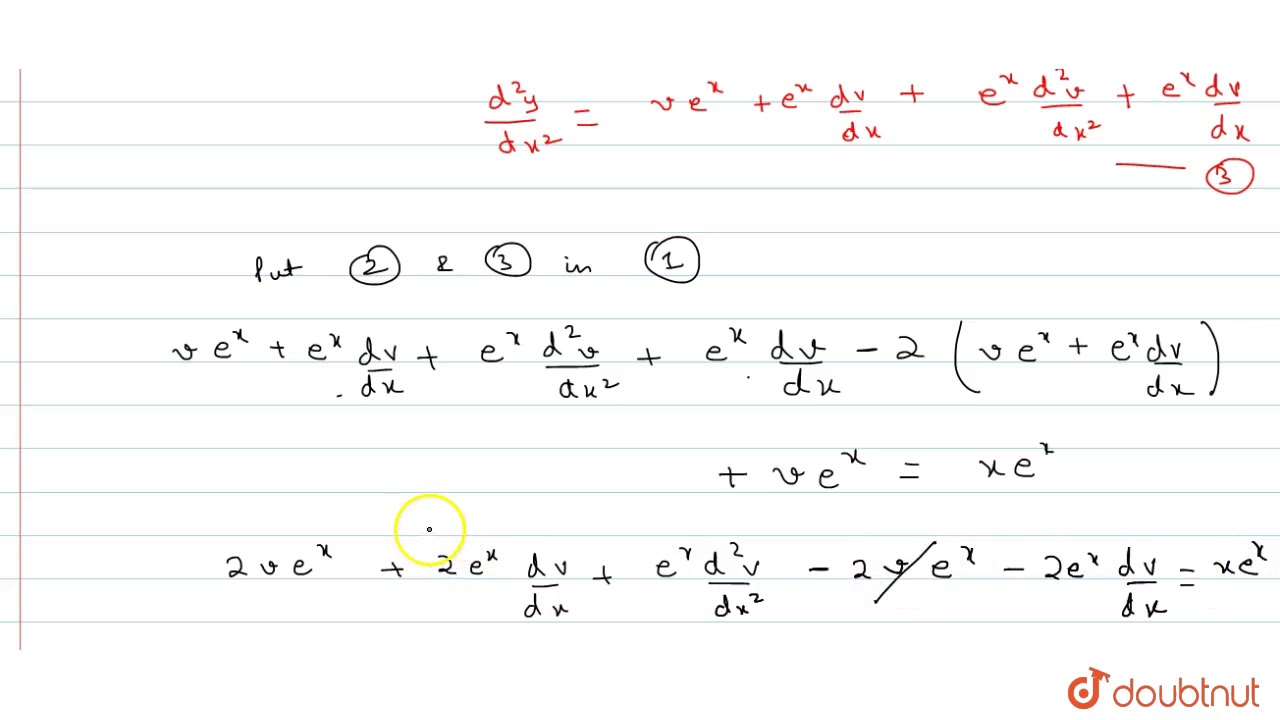 | ||
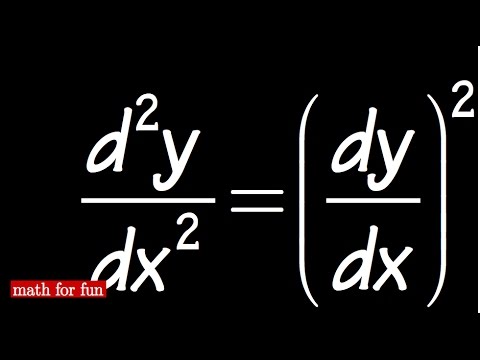 |  |  |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 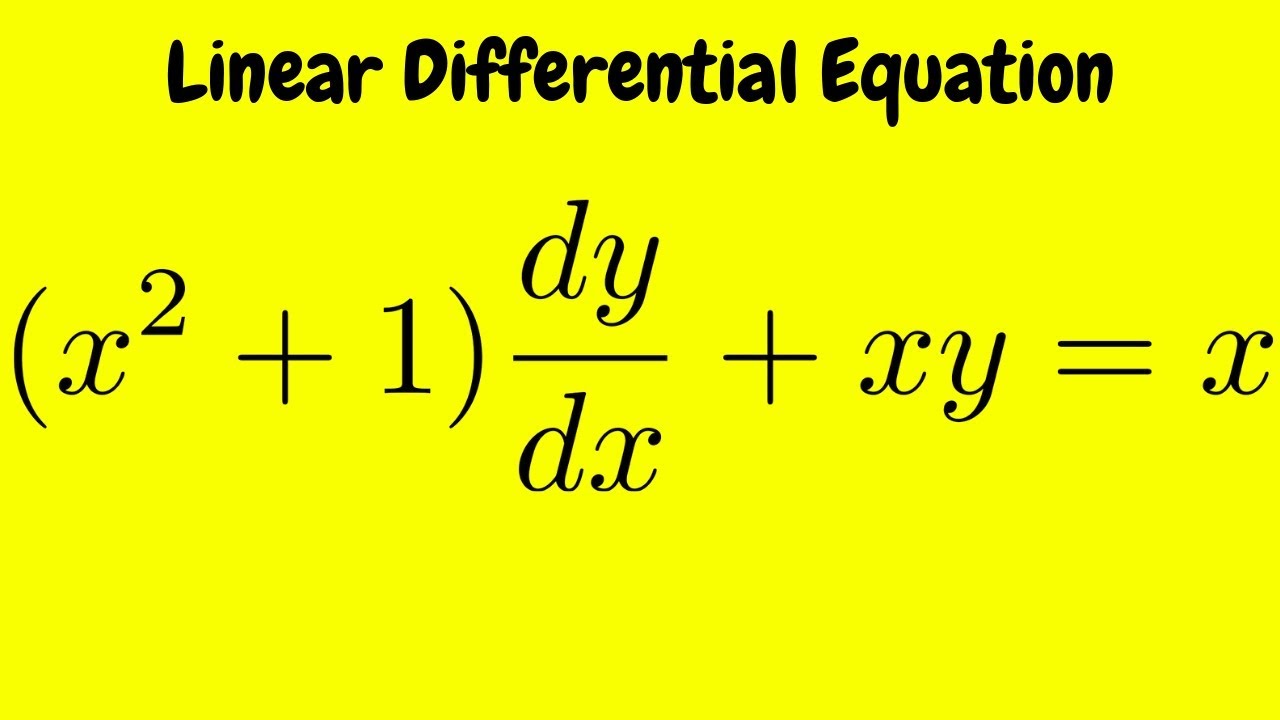 | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | 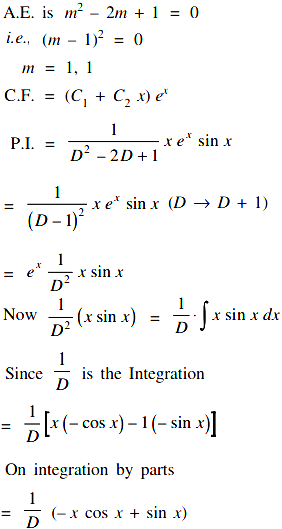 |  |
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 | ||
「D^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |
Answer d 2 y/dx 2 = e2x dy/dx = e 2x /2 c y= e2x /4 cx d The correct option is CSolve by Method of Variation of Parameters D 2 Y D X 2 3 D Y D X 2 Y = E E X University of Mumbai BE Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering Semester 2 (FE First Year) (d^2y)/dx^23 dy/dx2y=e^(e"^x)` Advertisement Remove all ads Solution Show Solution
Incoming Term: d^2y/dx^2-y=2/1+e^x, d^2y/dx^2+dy/dx+y=(1-e^x)^2, (d^(2)y)/(dx^(2))-3(dy)/(dx)+2y=(1)/(1+e^(-x)), e^(y)(x+1)=1 (d^(2y)/(dx^(2))=((dy)/(dx))^(2), solve (d^(2y)/(dx^(2))+(dy)/(dx)+y=(1-e^(x))^(2), 2(d^(3y)/(dx^(3))-3(d^(2y)/(dx^(2))+y=1+e^(x), 1. (d^(2y)/(dx^(2))-2x(dy)/(dx)+k^(2)y=e^(x),
コメント
コメントを投稿